Indexation problems are among the most frequent reasons why sites don’t rank in Google—even when producing excellent content. Without indexed pages, your site simply won’t appear in any searches, no matter how great your SEO efforts are.
Google Search Console (GSC) is the best tool for identifying and rectifying these issues. In this post, you’ll walk through the process of fixing indexing problems in Google Search Console, even if you’re a beginner.
What Are Indexing Issues on Google Search Console?
Indexing problems happen when Google won’t or can’t include your page in its search index. When a page isn’t indexed, it won’t rank or receive organic traffic.
In Google Search Console, such issues appear under:
Pages → Why pages aren’t indexed
Each issue is labeled clearly by Google, making it easier to fix – if you understand what they mean.
Why It’s Important to Fix Indexing Issues for SEO
Neglecting indexing issues can severely impact your site’s growth.
Here’s why fixing them matters:
- Pages won’t appear on Google
- New content won’t rank
- Crawl budget gets wasted
- SEO efforts show no results
- Google may view your site as low-quality
If you want steady traffic, ensuring your pages are indexed is essential.
How to Check Indexing Issues in Google Search Console
Before you fix anything, first identify the problem.
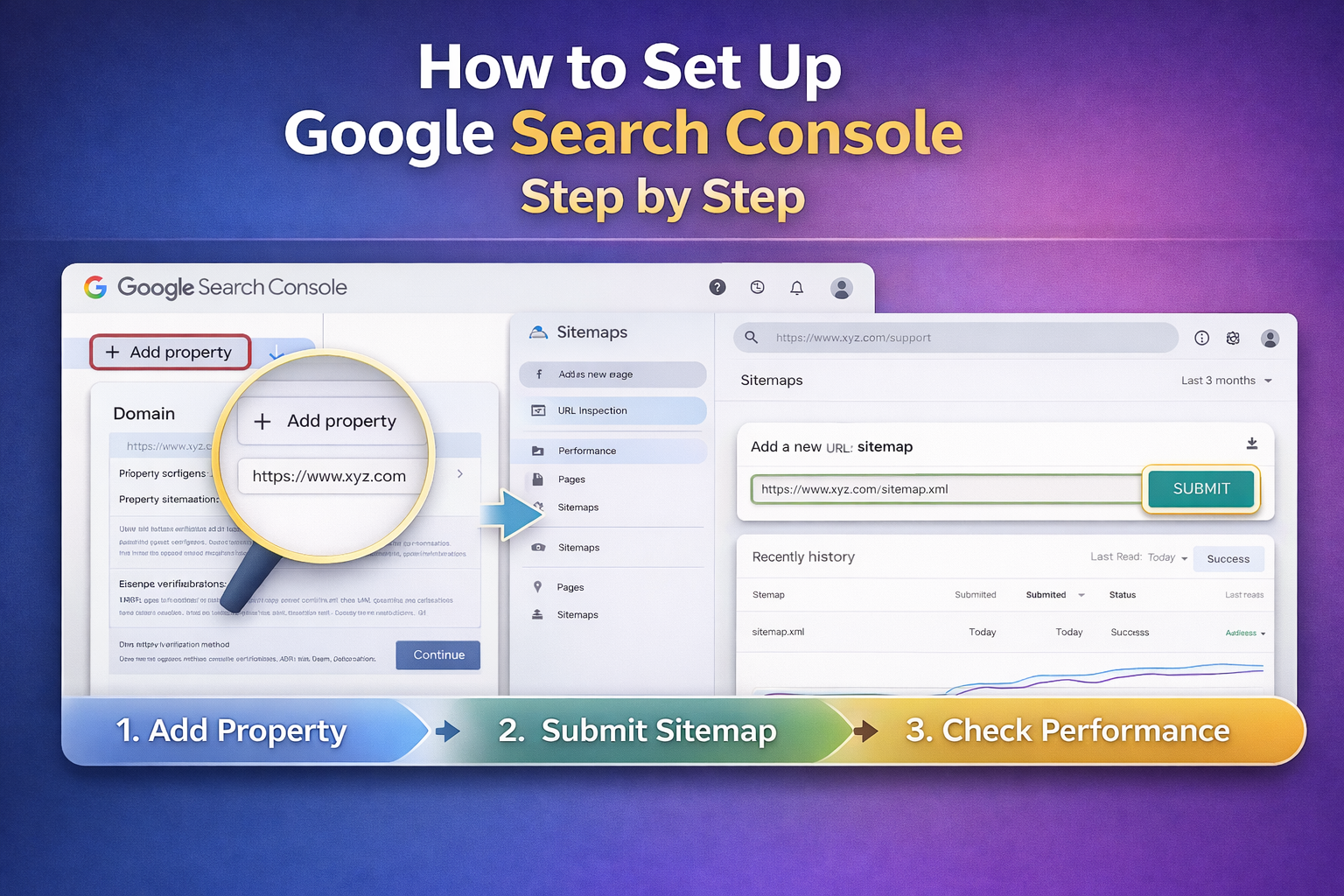
Step 1: Open Google Search Console and select your website property.
Step 2: Go to Indexing → Pages
Step 3: Review “Not Indexed” Pages and click the error type to see affected URLs and Google’s explanation.
Common Indexing Issues in Google Search Console (and How to Fix Them)
1. Crawled – Currently Not Indexed
What it means: Google crawled the page but didn’t index it.
Why it happens:
- Thin or duplicate content
- Low-quality pages
- Weak internal linking
- Poor user experience
Fix:
- Improve content depth
- Add internal links from related pages
- Remove duplicates
- Make sure the page satisfies search intent
- Request indexing after improving
2. Discovered – Currently Not Indexed
What it means: Google knows the page exists but hasn’t crawled it.
Why it happens:
- Crawl budget limits
- Poor internal linking
- Too many URLs
Fix:
- Add to XML sitemap
- Strengthen internal linking
- Avoid unnecessary URLs (filters, tags)
- Improve server speed
3. Page with Redirect
What it means: The URL redirects, so Google indexes the final page.
When okay: Intentional 301 redirects or restructuring.
Fix when needed:
- Avoid redirect chains
- Use a single 301 redirect
- Update internal links to the final URL
4. Excluded by ‘noindex’ Tag
What it means: Google detected a “noindex” directive.
Fix:
- Remove “noindex” if the page should rank
- Check SEO plugin settings
- Re-submit URL for indexing
5. Blocked by robots.txt
What it means: Google is blocked from crawling the page.
Fix:
- Open robots.txt and remove blocked directives
- Test in GSC’s robots.txt tester
- Request indexing
6. Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical
What it means: Google found similar pages and chose one itself.
Fix:
- Add proper canonical tags
- Merge duplicate content
- Avoid parameter-based URLs
How to Use the URL Inspection Tool
Paste the URL into the GSC search bar to:
- Check indexing status
- Review crawl details
- Request indexing after fixes
Best Practices to Prevent Indexing Issues
- Submit XML Sitemap Properly – keep it updated and include only indexable URLs.
- Improve Internal Linking – ensure every important page is linked.
- Avoid Thin Content – provide unique, valuable content.
- Keep Website Fast – slow pages reduce crawl frequency.
- Fix Technical Errors Regularly – monitor for server issues, mobile usability, and Core Web Vitals.
How Long Does Google Take to Index Pages?
There’s no set time—new pages can take hours to days, large sites longer, and low-quality pages may never be indexed. Quality and SEO consistency help speed things up.
Final Checklist
✔ Review Pages report often
✔ Fix technical blocks
✔ Improve content quality
✔ Strengthen internal linking
✔ Use canonical tags
✔ Submit sitemap
✔ Request indexing after updates
Final Thoughts
Fixing indexing issues in Google Search Console isn’t about shortcuts – it’s about maintaining quality, clarity, and consistency. When Google sees real value in your pages, indexing follows naturally.
If you stay consistent with these best practices, your pages will not only be indexed but also rank higher over time.
FAQs
Why isn’t Google indexing my pages?
Possible causes: low-quality content, technical errors, duplicates, or crawl limits.
Should I request indexing for every page?
No – only after fixing issues. Overusing it doesn’t help.
Is “Crawled – currently not indexed” bad?
Not a penalty – it just means Google doesn’t yet see enough value.
Do indexing issues affect rankings?
Yes. If pages aren’t indexed, they can’t rank.
Does deleting pages help indexing?
Sometimes – removing low-quality or duplicate pages can improve crawl efficiency.